A Forwarder is a DNS Server to which other DNS Server forward queries.
Types of Forwarders
o Standard
o Conditional
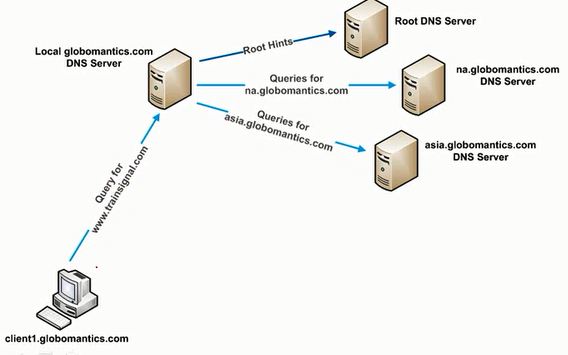
Conditional Forwarder: A conditional forwarder is a DNS server on a network that is used to forward DNS queries according to the DNS domain name in the query. For example, a DNS server can be configured to forward all the queries it receives for names ending with widgets.example.com to the IP address of a specific DNS server or to the IP addresses of multiple DNS servers.
Below figure shows how conditional forwarder is working.
Setting up a Conditional Forwarder:
Types of Forwarders
o Standard
o Conditional
Conditional Forwarder: A conditional forwarder is a DNS server on a network that is used to forward DNS queries according to the DNS domain name in the query. For example, a DNS server can be configured to forward all the queries it receives for names ending with widgets.example.com to the IP address of a specific DNS server or to the IP addresses of multiple DNS servers.
Below figure shows how conditional forwarder is working.
Setting up a Conditional Forwarder:
1. Start -> Administrative Tools -> DNS
2. Right Click Conditional Forwarders -> Select New Conditional Forwarder.
3. Type the Condition and IP of appropriate DNS Server, Then Click OK
Eg: Here i have given infotech.com as my condition, If any query which is looking for infotech domain then the query will pass to 192.168.5.2 DNS Server.